The individuals who appear are for illustrative purposes. All persons depicted are models and not real patients.
Those who choose VARIBAR® know the power of preparation in clinical practice. This also means the power that comes with transparent information exchange for our customers.
We invite you to explore this key information and data on everything from standardization and dysphagia to white papers, videos, and links for resources.
Explore the POWER of VARIBAR® (barium sulfate)
through its Standardization, Evidence, and Legacy
Standardization
Evidence
Legacy
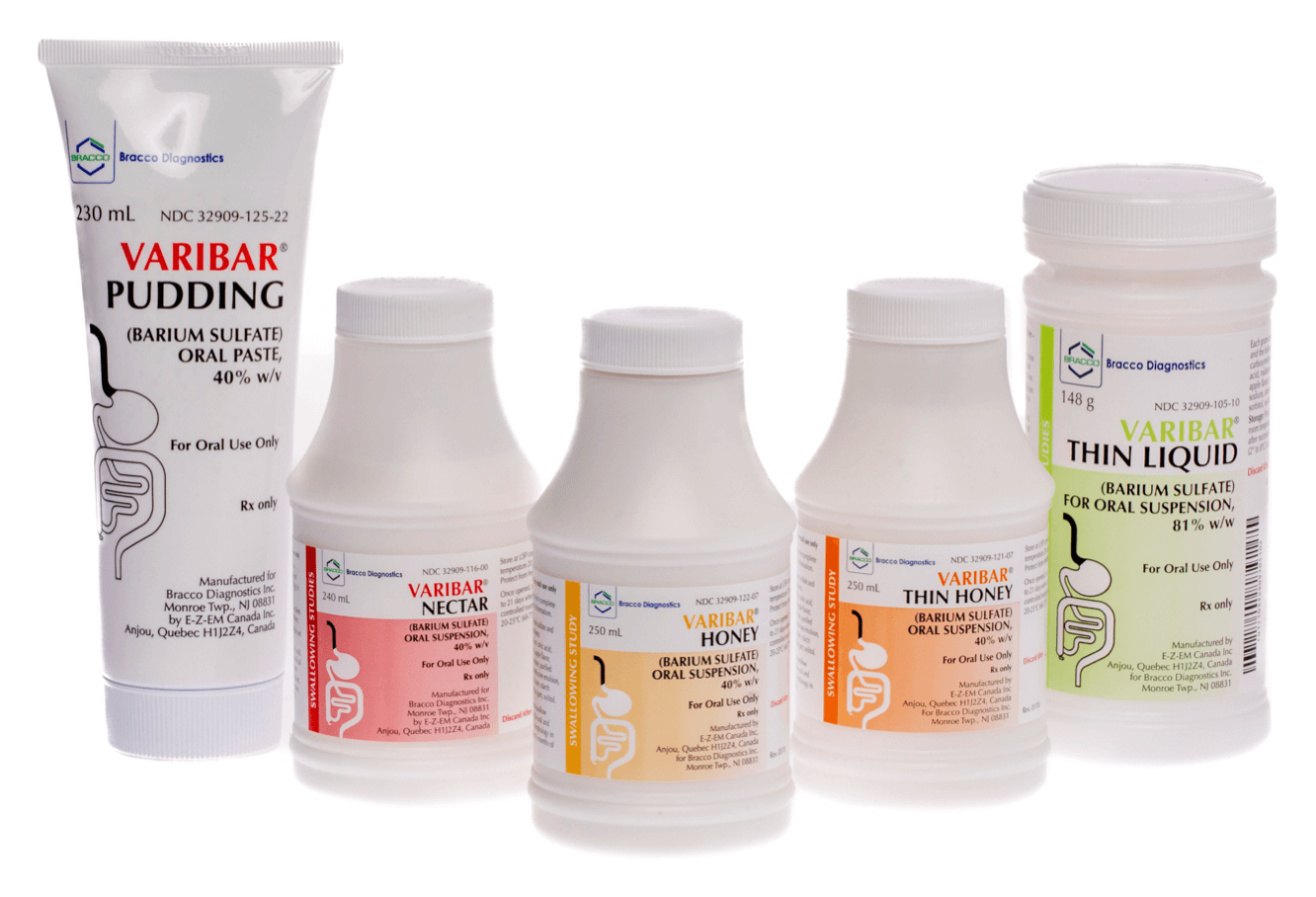
VARIBAR® (barium sulfate)
The ONLY premixed,* premeasured, and precise barium products for Modified Barium Swallow Studies (MBSS).¹
- VARIBAR® THIN LIQUID (barium sulfate) for oral suspension (148 g)
- VARIBAR® NECTAR (barium sulfate) oral suspension (240 mL)
- VARIBAR® THIN HONEY (barium sulfate) oral suspension (250 mL)
- VARIBAR® HONEY (barium sulfate) oral suspension (250 mL)
- VARIBAR® PUDDING (barium sulfate) oral paste (230 mL)
*VARIBAR® THIN LIQUID (barium sulfate) for oral suspension is supplied as a powder and reconstituted to a standard volume with water.

VARIBAR® (barium sulfate)MINIS
The same FDA‐approved products clinicians use for their standardized and validated MBSS… only smaller.
- VARIBAR® NECTAR (barium sulfate) oral suspension (70 mL)
- VARIBAR® THIN HONEY (barium sulfate) oral suspension (30 mL)
- VARIBAR® HONEY (barium sulfate) oral suspension (30 mL)
- VARIBAR® PUDDING (barium sulfate) oral paste (30 mL)
The POWER of Standardization
A lack of standardization may result in suboptimal diagnosis²
Standardization Helps Helps Ensure Reliable Results…
Patient
- Created for patients with agreeable flavors3
- Accurate measurement of progress on re-test1
- Enhanced safety due to premixed formulation4
- FDA approved for adult and pediatric patients1
- Reduces the need for repeat examinations1

SLP
- Reproducibility of results1,3
- Supports evidence-based practice1,3
- Increased efficiency and ease of use4
- Systematically designed for MBSS11,3
- Reduces the need for repeat examinations1

Radiologist
- Reproducibility of results1,3
- Consistent density (40%w/v) for optimal visualization3
- Enhanced safety due to premixed formulation4
- Procedure efficiency4
- Reduces the need for repeat examinations, which can reduce lifetime radiation exposure1,2
Lack of standardization can impede understanding of the actual results of treatment, produce ambiguous reporting of outcomes, and hinder understanding of restorative and rehabilitative targets²
Developing standards for the MBSS is a key concern throughout the Speech/Language Pathology (SLP) community. VARIBAR products were developed in cooperation with SLPs to help standardize diagnostic materials for accurate comparisons between studies.2,3
The POWER of Evidence
Evidence, rather than opinion, should guide clinical decision-making with standardized instruments, data collection protocols, analysis of test results, and reporting.²
Time-Tested and Trusted—A Legacy of Stability and Consistency
Standardized viscosities help eliminate the unpredictability of varied barium preparations²
Part of Evidence-Based Practice in the MBSS
Please visit our Insights page to find information about MBSS best practices.

VARIBAR products are formulated with standardized viscosities to support consistent, reproducible swallow studies grounded in the latest clinical evidence.1,3,4
The POWER of Legacy
Born in research, created with clinicians, designed for patients. VARIBAR® (barium sulfate) is the only FDA-approved and indicated barium sulfate product for the MBSS.
A Story of Standardization
“We started Protocol 201 with the idea that nectar was nectar and honey was honey, but when we asked the clinicians to bring in what they were using [in swallow studies] it was all over the place, even within the same facility. They were doing the best they could, but it just wasn’t comparable.” —Jackie Hind
In the late 90’s, Dr. JoAnne Robbins and Dr. Jeri Logemann were in the planning stages of a massive undertaking: a multi-site research project examining the effectiveness of interventions to prevent aspiration.4 This research, funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), would eventually include over 600 patients, 201 clinicians, and nine regional principal investigators, and would become known throughout the field of swallowing and dysphagia as Protocol 201.6,7
They encountered a barrier when they realized that facilities were using various “recipes” to mix existing barium sulfate products…which meant that the data from these different MBSS could not be compared accurately. There were additional concerns regarding the coating properties of existing products, which could be interpreted as residue by clinicians (J. Robbins, personal communication, September 18, 2024).
A Call for Consistency
“My favorite moment was when we informed the E-Z-EM people that we did not want the barium to adhere to mucosa. They didn’t understand the concept.” —Dr. James Coyle, Ph.D., CCC‑SLP, BCS‑S, F‑ASHA
With this realization that our field desperately required standardization of material used in the MBSS for not only this massive clinical trial, but also so that practicing clinicians could accurately assess their patients, the researchers approached E-Z-EM, a manufacturer of barium sulfate in Montreal, Canada, with the specifications needed to evaluate swallowing—standardized barium density, standardized viscosities, no coating of the mucosa, and palatability.3
Research and Development
“We collected so many samples from clinicians in the field, testing and comparing to what was being created in the lab.” —Dr. Mark Nicosia, Ph.D.
The scientists at E-Z-EM collaborated with the skilled team of researchers in Dr. Robbins’ lab, collecting information from clinicians in the field to determine and design the consistencies needed for an MBSS (M. Nicosia, personal communication, September 15, 2024). E-Z-EM eventually produced the original line of VARIBAR® (barium sulfate) products, and these were used in the research study.7,8
Meeting Clinician Needs
“Before VARIBAR, SLPs were doing all sorts of things. They were thickening, they were thinning, they were sometimes giving patients whatever they said they liked to eat. It was kind of crazy.” —Dr. JoAnne Robbins, Ph.D., ASHA Honors
But the story of VARIBAR and its dedication to meeting clinician needs doesn’t end there: In 2005, another consistency was added after repeated clinician requests for a product that fell into a viscosity category between Nectar and Honey.9 Back to the lab for the E-Z-EM scientists, and Thin Honey was born—a 1500cP product, supported by research and clinician need.
The VARIBAR Story Continues
“Reproducible patient and clinician experiences and outcomes were key drivers leading to the development and validation of a standardized method for videofluoroscopic swallowing assessment (MBSImP™©). Our team was fortunate to borrow from the successes of Drs. Robbins and Logemann, who worked with industry partners to standardize a core set of barium consistencies customized for the MBS—the VARIBAR line.” —Dr. Bonnie Martin-Harris, Ph.D., CCC‑SLP, BCS‑S, ASHA Honors
Bracco Diagnostics Inc. acquired E-Z-EM in 2008 and the VARIBAR story continues to be told—from its use in Dr. Bonnie Martin-Harris’ standardized and validated Modified Barium Swallow Impairment Profile (MBSImP™©)2 to our line of VARIBAR MINIS, we are proud of our history and excited about our future.

From the early days of MBSS to today’s standardized and validated protocols, VARIBAR has been the trusted product clinicians rely on for precision and consistency when conducting swallow studies.1-3,5-7
INDICATIONS AND USAGE | IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
VARIBAR® (barium sulfate)
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION:
For Oral Administration. This product should not be used in patients with known or suspected perforation of the GI tract, known obstruction of the GI tract, high risk of aspiration, or hypersensitivity to barium sulfate products. Rarely, severe allergic reactions of anaphylactoid nature have been reported following administration of barium sulfate contrast agents. Aspiration may occur during the modified barium swallow examination, monitor the patient for aspiration.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE | IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
VARIBAR® (barium sulfate)
INDICATIONS
VARIBAR® THIN HONEY (barium sulfate) oral suspension, VARIBAR® NECTAR (barium sulfate) oral suspension, and VARIBAR® THIN LIQUID (barium sulfate) oral suspension are radiographic contrast agents indicated for use in modified barium swallow examinations to evaluate the oral and pharyngeal function and morphology in adult and pediatric patients.
VARIBAR® HONEY (barium sulfate) oral suspension and VARIBAR® PUDDING (barium sulfate) oral paste are radiographic contrast agents indicated for use in modified barium swallow examinations to evaluate the oral and pharyngeal function and morphology in adult and pediatric patients 6 months of age and older.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
CONTRAINDICATIONS
These products should not be used in patients with known or suspected perforation of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract; known obstruction of the GI tract; high risk of GI perforation such as those with a recent GI perforation, acute GI hemorrhage or ischemia, toxic megacolon, severe ileus, post GI surgery or biopsy, acute GI injury or burn, or recent radiotherapy to the pelvis; high risk of aspiration such as those with known or suspected tracheo-esophageal fistula or obtundation; known severe hypersensitivity to barium sulfate or any of the excipients of the product used.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Barium sulfate preparations contain a number of excipients, including natural and artificial flavors, and may induce serious hypersensitivity reactions. The manifestations include hypotension, bronchospasm and other respiratory impairments, and dermal reactions including rashes, urticaria, and itching. A history of bronchial asthma, atopy, food allergies, or a previous reaction to a contrast agent may increase the risk for hypersensitivity reactions. Emergency equipment and trained personnel should be immediately available for treatment of a hypersensitivity reaction.
Intra-abdominal Barium Leakage
The use of VARIBAR PRODUCTS is contraindicated in patients at high risk of perforation of the GI tract. Administration of VARIBAR PRODUCTS may result in leakage of barium from the GI tract in the presence of conditions such as carcinomas, GI fistula, inflammatory bowel disease, gastric or duodenal ulcer, appendicitis, or diverticulitis, and in patients with a severe stenosis at any level of the GI tract, especially if it is distal to the stomach. The barium leakage has been associated with peritonitis and granuloma formation.
Delayed Gastrointestinal Transit and Obstruction
Orally administered barium sulfate may accumulate proximal to a constricting lesion of the colon, causing obstruction or impaction with development of baroliths (inspissated barium associated with feces) and may lead to abdominal pain, appendicitis, bowel obstruction, or rarely perforation. Patients with the following conditions are at higher risk for developing obstruction or baroliths: severe stenosis at any level of the GI tract, impaired GI motility, electrolyte imbalance, dehydration, on a low residue diet, taking medications that delay GI motility, constipation, pediatric patients with cystic fibrosis or Hirschsprung disease, and the elderly. To reduce the risk of delayed GI transit and obstruction, patients should maintain adequate hydration after the barium sulfate procedure. When administering VARIBAR PUDDING, consider the administration of laxatives.
Aspiration Pneumonitis
The use of VARIBAR PRODUCTS is contraindicated in patients with trachea-esophageal fistula. Oral administration of barium is associated with aspiration pneumonitis, especially in patients with a history of food aspiration or with compromised swallowing mechanism. Vomiting following oral administration of barium sulfate may lead to aspiration pneumonitis. In patients at risk for aspiration, begin the procedure with a small ingested volume of VARIBAR PRODUCTS. Monitor the patient closely for aspiration, discontinue administration of VARIBAR PRODUCTS if aspiration is suspected, and monitor for development of aspiration pneumonitis.
Systemic Embolization
Barium sulfate products may occasionally intravasate into the venous drainage of the GI tract and enter the circulation as a "barium embolus" leading to potentially fatal complications which include systemic and pulmonary embolism, disseminated intravascular coagulation, septicemia and prolonged severe hypotension. Although this complication is exceedingly uncommon after oral administration of a barium sulfate suspension, monitor patients for potential intravasation when administering barium sulfate.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramping. Serious adverse reactions and fatalities include aspiration pneumonitis, barium sulfate impaction, intestinal perforation with consequent peritonitis and granuloma formation, vasovagal and syncopal episodes.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information for VARIBAR® THIN LIQUID (barium sulfate) oral suspension.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information for VARIBAR® THIN HONEY (barium sulfate) oral suspension.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information for VARIBAR® NECTAR (barium sulfate) oral suspension.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information for VARIBAR® HONEY (barium sulfate) oral suspension.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information for VARIBAR® PUDDING (barium sulfate) oral paste.
VARIBAR is manufactured by E-Z-EM Canada Inc., for E-Z-EM, Inc., a subsidiary of Bracco Diagnostics Inc., Princeton, NJ 08540.
VARIBAR is a registered trademark of E-Z-EM, Inc.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE | IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
VARIBAR® (barium sulfate)
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION:
For Oral Administration. This product should not be used in patients with known or suspected perforation of the GI tract, known obstruction of the GI tract, high risk of aspiration, or hypersensitivity to barium sulfate products. Rarely, severe allergic reactions of anaphylactoid nature have been reported following administration of barium sulfate contrast agents. Aspiration may occur during the modified barium swallow examination, monitor the patient for aspiration.
References:
1. Martin-Harris B, Bonilha HS, Brodsky MB, et al. The modified barium swallow study for oropharyngeal dysphagia: recommendations from an interdisciplinary expert panel. Perspectives of the ASHA Special Interest Groups. 2021 Jun;6(3):610-619.
2. Martin-Harris B, Humphries K, Garand KL The Modified Barium Swallow Impairment Profile (MBSImP™©) – innovation, dissemination and implementation. Perspectives of the ASHA Special Interest Groups. 2017 Dec;2(4):129-138.
3. Robbins J, Nicosia M, Hind JA, et al. Defining physical properties of fluids for dysphagia evaluation and treatment. Perspectives on Swallowing and Swallowing Disorders (Dysphagia). 2002 Jun;11(2):16-19.
4. Steele CM, Martin-Harris B, Gosa M, et al. Diagnosis and management of swallowing physiology: standardized contrast, the MBSImP™, & the IDDSI framework. Published May 1, 2021. https://appliedradiology.com/articles/diagnosis-and-management-of-swallowing-physiology-standardized-contrast-the-mbsimp-the-iddsi-framework. Accessed March 6, 2025.
5. Robbins J. Protocol 201: a NIDCD-funded multisite clinical trial in swallowing. Perspectives on Swallowing and Swallowing Disorders (Dysphagia). 2000 Jul;9(2):2-3. https://doi.org/10.1044/sasd9.2.2
6. Robbins J, Hind J, Logemann J. An ongoing randomized clinical trial in dysphagia. Journal of Communication Disorders. 2004 Sep-Oct;37(5):425-435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcomdis.2004.04.006
7. Robbins J, Gensler G, Hind J, et al. Comparison of 2 interventions for liquid aspiration on pneumonia incidence: a randomized trial. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2008 Apr;148(7):509-518. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-148-7-200804010-00007
8. Logemann JA, Gensler G, Robbins J, et al. A randomized study of three interventions for aspiration of thin liquids in patients with dementia or Parkinson’s disease. JSLHR. 2008 Feb;51(1):173-183. https://doi.org/10.1044/1092-4388(2008/013)
9. Data on File. Bracco Diagnostics Inc.: 2005.